“Tobacco”
Tobacco, common name of several plants in the Nicotiana genus and Solanaceae family, first discovered by the native people of Mesoamerica and South America. It was brought to India by the Portuguese around 400 years ago. It had been in use since as early as 5000-3000 BC for recreational and medicinal purposes and in religious ceremonies. The tobacco kick, despite its harmful effect eventually grew up to be soo popular that in 2008, WHO declared tobacco as the single greatest preventable cause of death.
Why the tobacco kick?
Nicotine, the primary reinforcing component of tobacco gives the tobacco kick and drives tobacco addiction. Consumable tobacco contains 7000 more chemicals to add to the flavor and effect of nicotine.
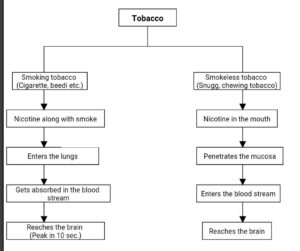
How we get the tobacco addiction?
In order to understand why do we get addicted to tobacco we need to understand the effect of tobacco on our brain, making it a craving rather than just a mode of pleasure. Tobacco after reaching the brain activates the following processes in our body:-
- The tobacco hit causes stimulation of adrenals and release of adrenaline which in turn increases blood pressure, respiratory rate and heart rate.
- It activates reward pathways, that regulates reinforcement and feelings of pleasure, releasing increased amounts of neurotransmitter dopamine and alters circuits involved in learning, stress and self control.
- Besides, it increases levels of Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine. Norepinephrine increases memory and concentration.
- There is also increases beta-endorphins reducing individual’s anxiety levels.
The effects of nicotine dissipate as quickly as their onset, reducing the associated feelings of reward. This causes the individual to continue dosing to maintain drug’s pleasurable effects and prevent withdrawal symptoms. The continued exposure to these effects causes long term brain changes resulting in withdrawal symptoms and addiction.
Adverse effects of tobacco
Tobacco consumption affects almost every system of the body. It enters into the blood stream and then dissipates to various parts of the body Interfering with the functions of various systems. Smoking, on the other hand not only harms the individual practicing it, but also people around them. Inhalation of a the tobacco smoke by a person other than the active smoker, known as passive smoking, equally affects the other person’s body. Infact, every time a person smokes, the products get deposited in the lungs which even in the absence of smoking, continuously keeps exerting its effects known as third hand smoking. The effect on various systems are as follows:-
- Respiratory system: Decreased lung function, breathlessness, build up of poisonous substances within the lungs, permanent damage to air sacs, initiation of lung damage.
- Circulatory system: Increased clotting tendency, atherosclerosis, enlargement of aorta.
- Brain: Dizziness, light headedness, irregular and disturbed sleep, nightmares.
- Gastrointestinal system: Xerostomia, Indigestion, peptic ulcer, nausea, vomiting.
- Heart: Heart rate and rhythm changes, increased blood pressure, increased risk of stroke.
- Immune system: Decreased levels of anti-oxidants, reduced immunity leading to longer duration of illness.
- Musculoskeletal system: tightening of muscles and reduction in bone density.
- Pregnancy: Behavioral issues, compromised brain development, increased incidence of Type 2 diabetes, weaker lungs, increased chances of cleft lip and cleft palate.
- Others: Premature wrinkling, increased risk of periodontitis.
- Reproductive system: Reduced fertility, menstrual cycle irregularities, early menopause.
Long term smoking results in following severe illnesses over time which can be proved fatal,
- Cancer of mouth, tongue, lungs, nose, larynx, tongue, etc.
- Lung diseases (Chronic obstructive lung disease, chronic bronchitis)
- Heart diseases and stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Alzheimer’s disease.
Withdrawal symptoms
With the continued use of tobacco a person’s body maintains a certain level of nicotine in the blood constantly, which results in addiction and withdrawal symptoms in case of absence of dosing or delayed dosing. According to American Heart Association, smoking tobacco is one of the hardest addictive substance to quit. The withdrawal symptoms in a person could range from craving, moodiness, difficulty in concentration, irritability, sense of emptiness to anxiety and depression. These symptoms, due to falling levels of nicotine in the brain and blood stream, usually begin within few hours of withdrawal and peaks within a day or two. They may last for a few days or weeks or even months in few cases but eventually subside. Moreover, according to some researchers, the severity and type of withdrawal symptoms even depends upon the genetic make-up of an individual.
Treatment for tobacco addiction
The treatment options for tobacco addiction are majorly non-pharmacological (not involving drugs) with one a few drugs available the use and efficacy of which are highly limited.
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy
The first and the best way to get rid of your tobacco addiction is the nicotine replacement therapy, where-in nicotine containing skin patches, nasal sprays, inhalers, solutions or gums are given to the patient gradually decreasing their dose. These contain nicotine in very small amounts to as compared to the smoking and chewing tobacco in order to suppress the urge and craving of the patient. These are gradually withdrawn to taper down the nicotine levels of blood and completely withdrawn when the withdrawal symptoms subside.
- Psychological counselling
Not a definitive treatment options, but an adjunctive treatment in order to double the chances of quitting the addiction. Psychological counselling by doctors or even family members and friends regarding the long-term effects can largely motivate a person to continue efforts at quitting.
- Pharmacological options
Certain drugs such a bupropion SR and vareniciline tartrate have been used to subside the tobacco urge with limited applications. However, these drugs should be used under the guidance of a physician only.
By – Dr. Shivani Dattani

